Dopamine, the neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that transmits information between neurons. Neurons are the basic functioning unit of our nervous system consisting of the spinal cord, nerves, and sensory organs like ears and eyes. The neurons control the movement of our body and help the brain to feel pleasure. Hence, dopamine is often referred to as the “feel-good hormone.”[1]
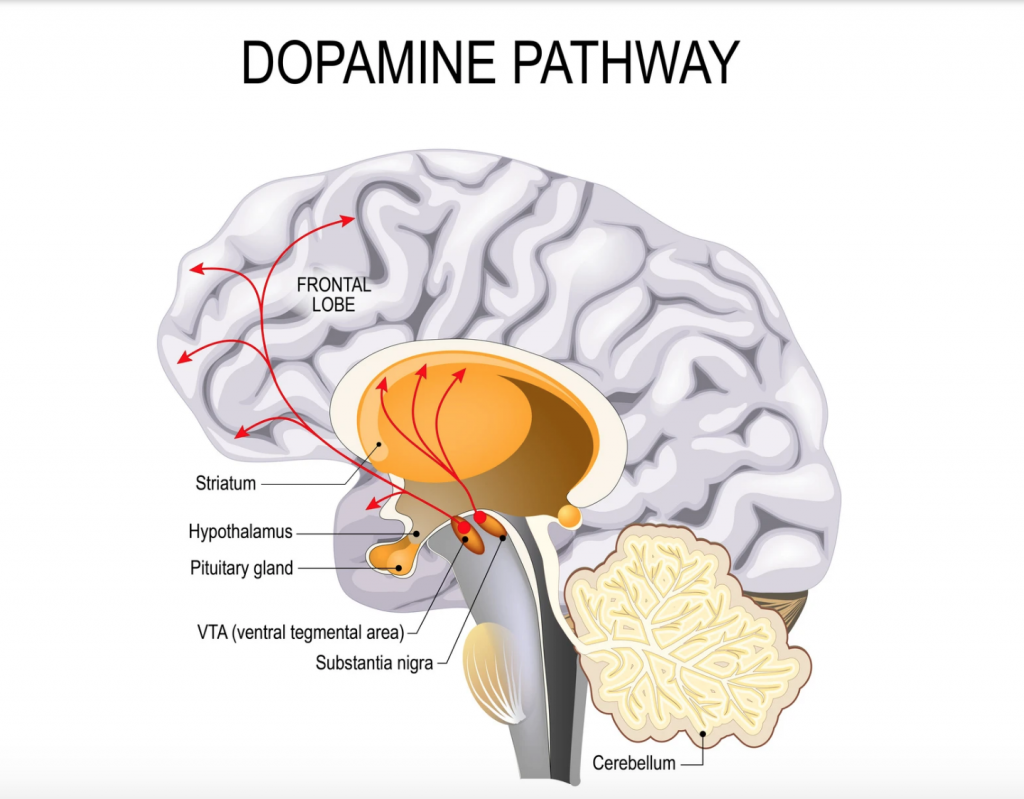
Dopamine is found in two different areas of the brain. Dopamine is rich in substantia nigra, which dies with the onset of Parkinson’s disease, thereby leading to mobility issues and even tremors.[2]
Dopamine is created by the ventral tegmental area and released into the body to feel pleasure and signaling. After dopamine is created in the brain, it is released in different body areas to feel emotions such as pleasure or rewards. Dopamine always doesn’t associate reward behaviors but also with necessary behaviors that are required for survival, such as eating and drinking water.
As always, too little or too much of something can be very harmful to overall health. Similarly, excessive and less dopamine can bring about many health issues, especially like Parkinson’s disease.
Dopamine and Movement
Dopamine produced in substantia nigra is responsible for controlling movement. The basal ganglia region of the brain is responsible for controlling body movement. They rely entirely on the dopamine-containing neurons for the secretion of dopamine to ensure proper functioning.[3]
But sometimes this secretion can be disrupted, and the required amount of dopamine fails to reach basal ganglia and substantia nigra. The failure of enough secretion of dopamine can increase the risk of improper or uncontrolled movement in the body, and it also affects the motor functioning of the body. Researches have shown that the lack of dopamine in the body can increase the risk of delayed or uncontrolled movements.
Sometimes basal ganglia may become overloaded with dopamine. In such cases, too, the movement will be limited or force the body to make a lot of movements, mostly unnecessary and uncontrolled (also a symptom for Tourette’s syndrome).[4]
Dopamine Basics
The brain follows a two-step process for the production of dopamine. The amino acid tyrosine is changed to dopa, which later on changes to dopamine.
Dopamine has a lot of impact on physical and mental behaviors such as
- Learning
- Heart rate
- Blood vessel functioning
- Lactation
- Sleep
- Kidney functioning
- Attention
- Mood
- Controlling nausea and vomiting
- Movement
Dopamine and addiction
Dopamine rush is pretty high when one takes in cocaine or drugs. This eventually increases the risk of drug addiction. When one uses drugs, dopamine secretion becomes exceptionally high, and hence, it is related to rewards and pleasures. This continuous feeling of pleasure and rewards will make one repeat the cycle to attain the same reward. This becomes an endless cycle, and eventually, one becomes addicted.[5]
But being addicted to drugs isn’t the only problem. Due to higher dopamine rush levels, people will want to take drugs in higher amounts to experience the same. After a certain point in time, the brain becomes used to and secretes less dopamine. This further has an impact on lowered pleasure levels. Drugs tend to cause a high release of dopamine.[6]
Since dopamine offers rewards and pleasures, one finds it very hard to break the addictive cycle. This addiction becomes so intense that it becomes almost impossible for people to overcome their addiction. Hence, a therapist or counselor can be of help to overcome addiction.
Dopamine and Mental Health
When it comes to mental health disorders, it is really tough to find out the exact cause of it. These mental health disorders are often considered to be consistent due to low levels of dopamine secretion by the brain.[7]
Schizophrenia
Researchers initially believed that schizophrenia happened due to a hyperactive dopamine system. However, it is entirely not responsible for this, but there are other chemical reactions too that affect the brain, such as delusions and hallucinations. Often schizophrenic people feel a lack of motivation and desire.
ADHD
The exact cause of ADHD or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is still unknown. But researchers believe that ADHD occurs mostly due to low levels of dopamine. Nonetheless, genetic disorders, too, can cause ADHD. ADHD is often treated using methylphenidate, which is known to boost dopamine levels.[8]
Dopamine and other diseases
As stated earlier, dopamine has a vital role to play in mental and physical health. It has an impact on Parkinson’s disease, but it also has an impact on obesity.[9]
Parkison’s disease
The onset of Parkinson’s disease leads to the degeneration of neurons, thereby disrupting control and movement. The body produces less dopamine, and the chemical imbalance is often visible through physical problems. Usually, medicines are prescribed to increase the level of dopamine in the body.
Obesity
Burning more calories than consuming can help reduce weight. But it isn’t that simple for obese people. Obese people have a disrupted reward system, which is why they may have disrupted feelings of satisfaction even before eating. Thus, studies have shown that obese people do not produce enough feel-good hormone “serotonin” and even dopamine.[10]
Dopamine is Helpful for living
Dopamine is one of the most important chemicals in our body. Needless to say, it acts as a lifesaver. Prescription dopamine is used by doctors in treatment for patients with conditions like
- Lack of heart to pump out enough blood
- Low blood pressure
- Reduced blood flow to essential organs
- Septic shock
However, dopamine may have counter-reactions when taken with certain medicines related to conditions like
- Chest pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Faster heart rate
- Irregular heartbeat
- Troubled breathing
Dopamine has a major impact on our mood and regulates body movements as well. It is necessary to keep a check with diet and lifestyle changes to boost dopamine levels naturally. A proper sleep schedule and healthy diet is the key to staying active and healthy.[11]
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539894/
[2] Rizo J. Mechanism of neurotransmitter release coming into focus. Protein Sci. 2018 Aug;27(8):1364-1391. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
[3] Herlenius E, Lagercrantz H. Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators during early human development. Early Hum. Dev. 2001 Oct;65(1):21-37. [PubMed]
[4] Zhou Y, Danbolt NC. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Aug;121(8):799-817. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
[5] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3860493/
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4085579/
[7] Bowery NG, Smart TG. GABA and glycine as neurotransmitters: a brief history. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147 Suppl 1:S109-19. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3479149/
[9] Ko JH, Strafella AP. Dopaminergic neurotransmission in the human brain: new lessons from perturbation and imaging. Neuroscientist. 2012 Apr;18(2):149-68. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
[10] Lau A, Tymianski M. Glutamate receptors, neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration. Pflugers Arch. 2010 Jul;460(2):525-42. [PubMed]

