Overview
The importance of folic acid in human life is undeniable. This vitamin is an absolute must for pregnant women. It is necessary for healthy fetal growth. Another reason is the prevention of multiple birth defects. Recent studies recommend regularly adding folates in your diet. This will lower your chances of suffering from high blood pressure. And that’s just the tip of the iceberg.[1]
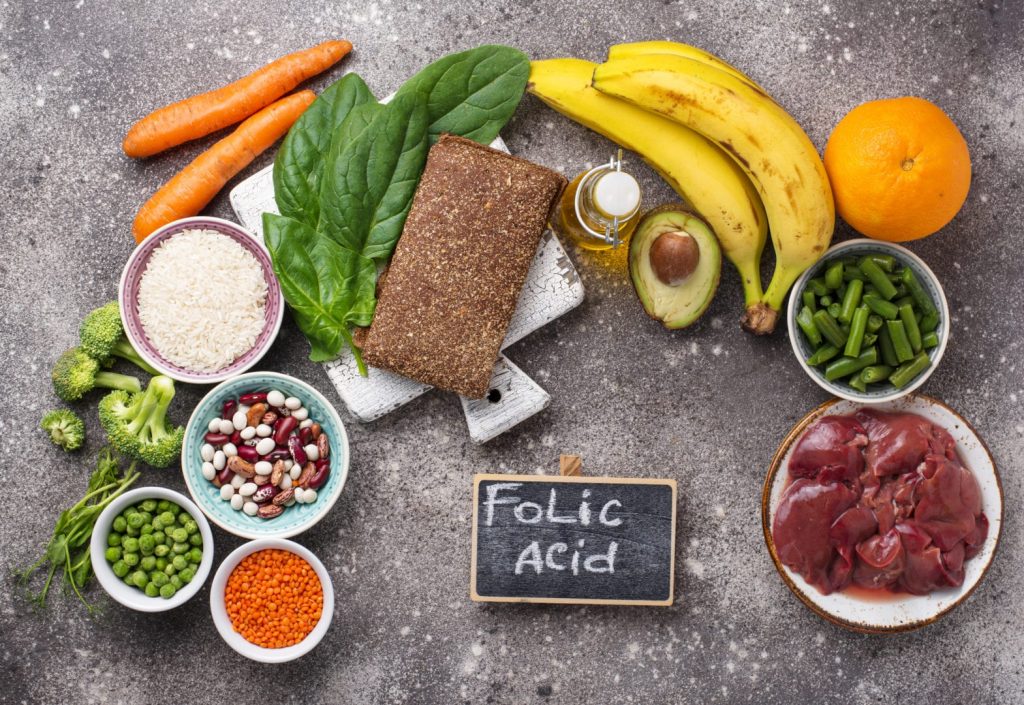

Chemical Composition and Availability
Folate is naturally available in several foods. The synthesized variant is commonly known as Folic Acid. Both are actually a water-soluble form of Vitamin B9. Members of the B family aid in glucose synthesis. Vitamin B9 additionally helps to manufacture DNA and RNA.[2]
Addition of folic acid in common food items is compulsory. Federal Law passed the resolution in 1998. Items including bread and bakery items, cereals, and many more. Green leafy vegetables (spinach, broccoli, lettuce, sprouts) have high concentrations of folate. Love fruits? Add avocado, banana or melons in your daily regimen. You can also opt for other sources like yeast, mushrooms, meat, or orange juice.[3]
You can also look for folic acid supplements. They are available both online and in local stores.
Importance
B-Complex vitamins kick starts the assimilation of fats and proteins. They are also necessary for the proper functioning of the liver. Longing for healthy-looking skin, hair, and eyes? Look towards Vitamin B.
Folic Acid is used up during the manufacture of DNA. Thus they are required during rapid body growth stages. Think about infancy, teenage or pregnancy. They are integral in the creation of RBCs (Red Blood Cells). Along with Vitamin B12, it ensures the proper usage of iron throughout our body.[4]
Folates work well in coordination with Vitamin B6, B12, and other micronutrients. This coordination regulates homocysteine content in the blood. Amino acid homocysteine leads to multiple organ ailments. Experts are unsure as to why.
Deficiency
Folate deficiency leads to serious adverse effects. The common causes of Vitamin B9 deficiency are alcoholism. IBD, or Inflammatory Bowel Disease and celiac disease can also reduce folic acid levels. Certain medicines may also cause this deficiency.
A lack of Vitamin B9 can cause a series of complications in our body.
The possible problems may include:
- Growth issues
- Tongue Inflammation
- Gingivitis
- Loss of hunger.
- Breathlessness
- Diarrhea
- Irritability and stunted brain functioning- including forgetfulness and sluggishness.

Why you should never neglect folic acid
· Prevention of multiple birth defects
It is bad for a pregnant woman to have a deficiency of folic acid. There is a high possibility that her newborn baby with have an arrested growth. Folic acid remarkably decreases any chances of NTDs (Neural Tube Defects). Neural Tube Birth Defects halter the brain development. It is also harmful for the infant’s spinal cord. Some of the common variants are spina finida, cleft palate, and brain damage. The most severe version of an NTD is a disease called anencephaly. The disease does not allow the brain to fully grow.[5]
A pregnant woman needs a daily uptake of 600 mcg of folic acid per day to ensure the healthy growth of her baby. Women planning to become pregnant should consume 400 mcg of folates per day- as neural tube defects can occur just after conception. Studies have shown that the neural birth defects can be reduced by as much as 72% to 100% by consuming the required daily folic acid intake during conception and the first trimester. Folic acid may also help in averting miscarriages. Prenatal folic acid supplements at the time of conception can be linked to lower risks of autism and better emotional growth.[6]
· Ensures healthy functioning of the heart
Folic acid is beneficial in for the heart- in more ways than one. Based on population studies, a sufficient folic acid intake in your diet can reduce heart ailments.[7]
As explained earlier, high levels of the amino acid homocysteine increase the possibility of coronary artery disease by 1.7 times. The chances of a stroke increases by 2.5 times with high levels of homocysteine. B complex vitamins, including folic acid, are essential for the reduction of homocysteine.
· Protects your eyes from AMD
Research studies found that the risk of developing age-related macular degeneration(AMD) can be reduced with regular intake of Vitamins B6, B9, and B12 in your diet. The large study had women consuming 2500 mcg of Vitamin B9(folic acid) with 500 mg of Vitamin B6 and 1000 mcg of Vitamin B12(Cyanocobalamin) daily. AMD is an eye disease with the potential of causing vision loss.[8]
· Reduced risk of Certain Cancer types
Based on large population studies, it has been found that an adequate amount of folic acid in your regular diet ensures a lower chance of certain cancer types. The types include cancer in the colon, breast, cervix, pancreas, and stomach region.
Researchers assume that the role of folic acid in ensuring healthy DNA aids in preventing possible can mutations. There is, however, no direct evidence linking folic acid supplements to stopping cancer.
Regular heavy drinking of alcohol raises the risk of breast cancer in women. An adequate amount of folic acid intake can reduce the effects of this risk- as seen in a study involving more than 50,000 women.[9]
· Beneficial for your kidneys
A high level of homocysteine is common among 85% of people with severe kidney issues, including End-Stage Renal Disease(ESRD). As Folic Acid is functional in reducing homocysteine levels, it is also good for people with severe kidney diseases.
· Other Benefits
Methotrexate is a powerful antimetabolite medication used to treat a variety of illnesses- including cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis. However, it also comes with a lot of side effects- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss/gain. The side effects of the chemotherapy drug are reduced by folic acid.[10]
Folic acid is also helpful in reducing gum defects among pregnant women or users of the anti-epileptic drug- phenytoin(Dilantin). The anticonvulsant drug used to control seizures can swell the gums and make it bleed- as a side-effect.
Besides, a few studies suggest that folic acid, in combination with anti-depressants aids in depression. It is also possibly effective against memory decline among older people.[11]
Dosage
General RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowances) For Folate.
Adults
- Men and Women 400mcg
- Pregnant Women 600mcg
- Lactating Women 500mcg
Children
- Infants (0-6 months) 65mcg
- Infants (7-12 months) 80 mcg
- Children (1-3 years) 150mcg
- Children (4-8 years) 200mcg
- Children (9-13 years) 300mcg
- Teens (14-18 years) 400mcg.
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554487/
[2] Scaglione F, Panzavolta G. Folate, folic acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate are not the same thing. Xenobiotica. 2014 May;44(5):480-8. [PubMed]
[3] van Gool JD, Hirche H, Lax H, De Schaepdrijver L. Folic acid and primary prevention of neural tube defects: A review. Reprod. Toxicol. 2018 Sep;80:73-84. [PubMed]
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535377/
[5] Li B, Zhang X, Peng X, Zhang S, Wang X, Zhu C. Folic Acid and Risk of Preterm Birth: A Meta-Analysis. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:1284. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5849489/
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2592326/
[8] Langan RC, Goodbred AJ. Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Recognition and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2017 Sep 15;96(6):384-389. [PubMed]
[9] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3218540/
[10] Skoutakis VA, Acchiardo SR, Meyer MC, Hatch FE. Folic acid dosage for chronic hemodialysis patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1975 Aug;18(2):200-4. [PubMed]
[11] Field MS, Stover PJ. Safety of folic acid. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018 Feb;1414(1):59-71. [PMC free article] [PubMed]